
Human Rights Oversight
A number of distinct monitoring bodies oversee States’ implementation of, and compliance with, their specific obligations under international human rights law. These monitoring bodies may be judicial (national, regional or international courts), quasi-judicial (bodies that are not courts, but do decide individual complaints), political (bodies led by States), or supervisory (bodies that document and assess human rights conditions). For an explanation of the history of these bodies, and the standards they enforce, see the Overview of the Human Rights Framework.
Jurisdiction and Geography
These tabs provide an overview of human rights oversight (i.e. oversight bodies and mechanisms) by jurisdiction and/or geography: (1) United Nations oversight, (2) regional oversight, (3) national oversight, and (4) other international oversight.
United Nations
At the universal level, the United Nations has established a number of institutions and procedures to monitor human rights in the 193 countries that belong to the UN. These mechanisms include the:
- United Nations human rights treaty bodies
- United Nations independent experts (special procedures)
- Universal Periodic Review
- United Nations Human Rights Council
In addition, the International Labour Organization (ILO) creates international standards related to workers’ rights and social justice issues, and supervises their implementation in the ILO’s 185 Member States.
Regional Oversight
At the regional level, intergovernmental organizations have established regional human rights systems, with widely different mandates, in each of the following regions:
- Africa
- the Americas
- Europe
- the Middle East
- Southeast Asia
Other Supranational Courts
The international community has also created a variety of other international courts and organizations that are not exclusively focused on international human rights standards, but whose work often addresses human rights concerns.
These include the International Court of Justice, which settles a wide variety of disputes between States, and the following courts that prosecute individuals for violations of international law:
National Oversight
Additionally, national governments may address human rights conditions and alleged violations through:
Other International Oversight
- International Court of Justice
- International Criminal Court
- International Criminal Tribunal for Rwanda
- International Criminal Tribunal for the former Yugoslavia
- Internationalized Criminal Tribunals
- International Labour Organization
- Courts and Tribunals of Regional Economic Communities
- Caribbean Court of Justice
- Central American Court of Justice
- Common Market for Eastern and Southern Africa Court of Justice
- Court of Justice of the Andean Community
- Court of Justice of the European Union
- East African Court of Justice
- Economic Community of West African States Court of Justice
- Southern African Development Community Tribunal
Treaties
Functions
This diagram provides an overview of the functions of key human rights oversight bodies. From the PDF, click on the names of an oversight body to learn more about it. This diagram was created by the International Justice Resource Center and was last updated in March, 2025.
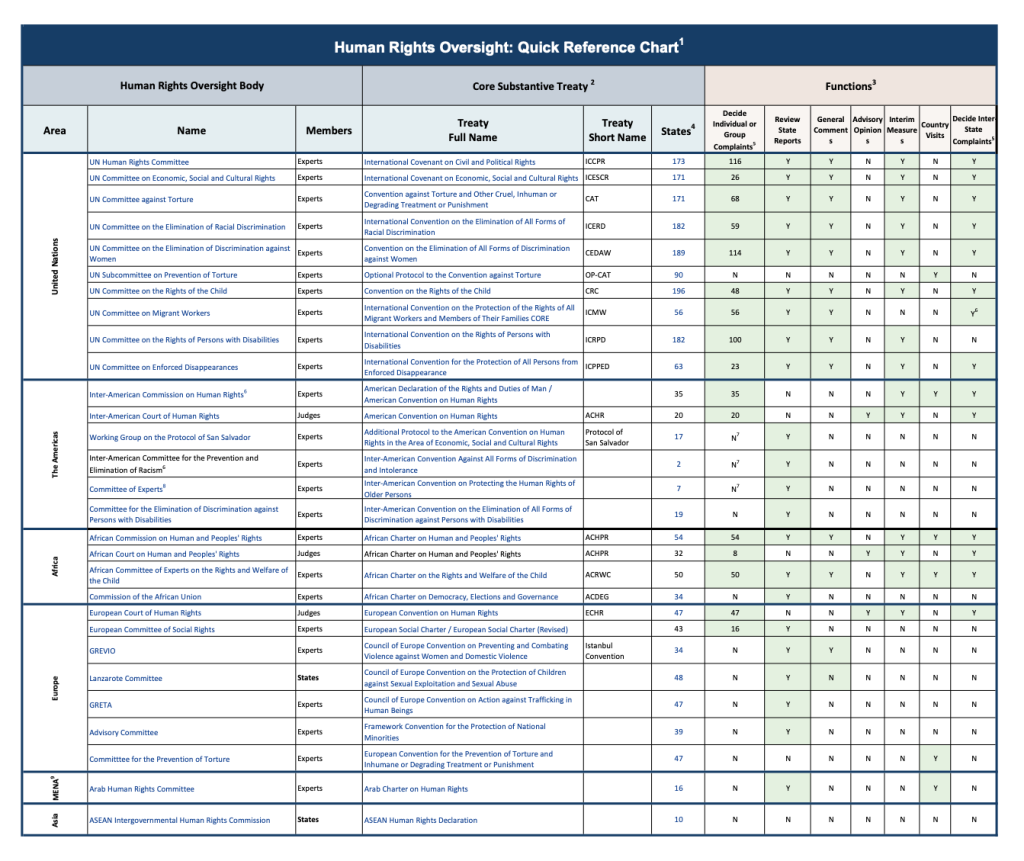
Quick Reference Chart
This chart provides an overview of (1) principle UN and regional human rights oversight bodies, (2) their composition, (3) the core substantive treaties for which these bodies are responsible, (4) the treaties’ short names (5) the competencies of the oversight bodies, and (5) links to additional information. This table was developed by the International Justice Resource Center and was last updated in March, 2025.
Stay Informed
Stay informed by subscribing to one or both of our mailing lists:
CGLJ News and CGLJ Resource Hub Newsroom!
